What is Bluetooth Low Energy?
What Is Bluetooth Low Energy - An Overview
BLE stands for Bluetooth Low Energy. It is a form of wireless communication designed especially for short-range communication. BLE is very similar to Wi-Fi in the sense that it allows devices to communicate with each other. However, BLE is meant for situations where battery life is preferred over high data transfer speeds.
Layers Of BLE
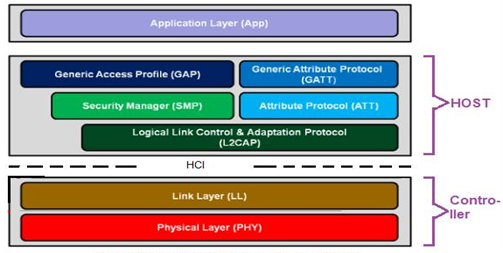
BLE is organized in a number of layers. Each layer has its purpose and plays a significant role in making a BLE device function properly. There are three building blocks of BLE.
Application Layer
Host Layer
Controller Layer
The Application: Is the highest layer and the one responsible for containing the logic, user interface, and data handling of everything related to the actual use-case that the application implements. The architecture of an application highly depends on the project developed with BLE.
The Host: Consists of the following layers
Generic Access Profile (GAP)
Generic Attribute Profile (GATT)
Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP)
Attribute Protocol (ATT)
Security Manager (SM)
Host Controller Interface (HCI), Host side
The Controller: Includes the following layers
Host Controller Interface (HCI), Controller side
Link Layer (LL)
Physical Layer (PHY)
Figure 2: BLE Protocol Stack
Characteristics In Bluetooth Low Energy
Characteristics are containers for user data. They always include at least two attributes: the characteristic declaration (which provides metadata about the actual user data) and the characteristic value (which is a full attribute that contains the user data in its value field).
Additionally, the characteristic value can be followed by descriptors, which further expand on the metadata contained in the characteristic declaration. The declaration, value, and any descriptors together form the characteristic definition, which is the bundle of attributes that make up a single characteristic.
The characteristic declaration attribute’s type UUID (0x2803) is a standardized, unique UUID used exclusively to denote the beginning of characteristics. As with all other declarations (such as service and include), this attribute has read-only permissions, because clients are allowed only to retrieve its value but in no case modify it.
Throughout Difference Between BLE 4 And BLE 5
Speed:
Bluetooth 5 is faster than Bluetooth 4 with the former having 2Mbps, twice the speed of the Bluetooth 4 of about 1Mbps making the Bluetooth 5 able to meet one of IoT requirements. This is thanks to the 5Mbps bandwidth of the Bluetooth 5 in comparison to 2.1Mbps of the Bluetooth 4.
Range:
Bluetooth 4 supports 50m in outdoor range and 10m in indoor range making it so low whilst Bluetooth 5 supports 200m in Line-of-Sight path in outdoor environment and 40m in indoor environment. Therefore, if someone wants to listen to music with wireless headsets while moving around the house or the courtyard, then the Bluetooth 5 will work best.
Power Requirement:
The Bluetooth 5 has been formulated to use less power on your device compared to the Bluetooth 4. That means you can keep your Bluetooth switched on for a longer period of time and do much more compared to Bluetooth 4 which consumes more power than its newer counterpart.
Message Capacity:
The Bluetooth 4 has a small message capacity of about 31bytes which gives just 17 to 20 bytes for actual data payload while the Bluetooth 5 with a large capacity of 255bytes gives more bytes for actual data payload.
Bluetooth Beacon:
With Bluetooth 5, beacons have become more popular due to the speed and range increase while with Bluetooth 4, they are less popular due to the less speed and range as well as low message capacity of 31bytes.
Support For IoT Devices:
Bluetooth 5 easily meets the requirements for IoT devices with its good range and increase in speed while Bluetooth 4 does not due to its low speed and short working range. That means IoT devices will work well with Bluetooth 5 and utilize all its features properly, for example the new Samsung Galaxy 8 and Galaxy 8+.
Compatibility:
Bluetooth 4 works best with devices that are compatible with version 4 series but will not work with devices that have Bluetooth 5 while Bluetooth 5 is backward compatible with v1, v2, v3, v4, v4.1 and version 4.2 but will not utilize all the features of Bluetooth 5.
Mesh Networking In BLE 4 And Added Feature In BLE 5
BLE 4 was introduced in 2010 and it did not have capability of mesh networking. It was capable of connecting with only one device at a time. Mesh networking was introduced back in 2017. Mesh networking was 1st added in BLE 5. BLE 5 mesh networking allows many-to-many (m:m) device communication and is optimal for the creation of networks on a large scale. It is ideal for environmental monitoring, automation asset tracking and IoT devices that require thousands of devices to communicate simultaneously.
Practical Uses Of Bluetooth Low Energy 5
With its low power consumption, inexpensive hardware, and small form factors, BLE5 provides scope for a wide range of applications. In previous iterations, Bluetooth Low Energy technology was largely used for storage, beacons, and other low-power devices, but came with some serious limitations. For instance, wireless headphones were unable to exchange messages under BLE4.
With Bluetooth 5.0, all audio devices can share data via Bluetooth Classic, and Bluetooth Low Energy is now more applicable for wearable devices, smart IoT devices, fitness monitoring equipment, and battery-powered accessories such as wireless keyboards.